Introduction
The ip command is a Linux networking tool for system and network administrators. IP stands for Internet Protocol and as the name suggests, the tool is used for configuring network interfaces.
Older Linux distributions used the ifconfig command, which operates similarly. However, ifconfig has a limited range of capabilities compared to the ip command.
In this tutorial, we go through all of the important operations the ip command can perform in Linux.

How to Use the ip Command
ip [OPTION] OBJECT {COMMAND | help}OBJECTS (or subcommands) that you will use most often include:
1. link (l) – used to display and modify network interfaces.
2. address (addr/a) – used to display and modify protocol addresses (IP, IPv6).
3. route (r) – used to display and alter the routing table.
4. neigh (n) – used to display and manipulate neighbor objects (ARP table).
There are many other objects and commands available. To see a full list type in the following command:
ip help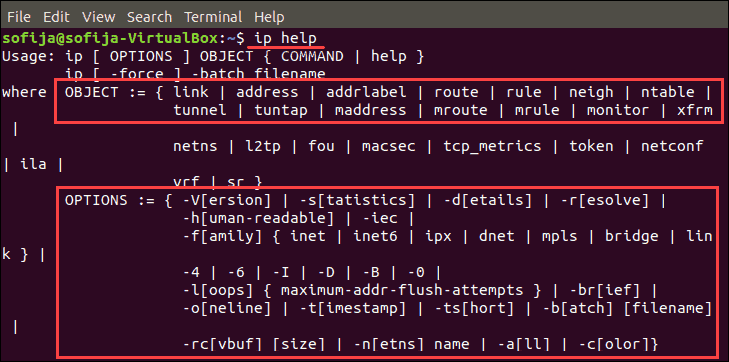
To execute commands, you can use either full or abbreviated forms. For example, ip link and ip l will give the same results.
When configuring network interfaces, you must run the commands as root or a user with sudo privileges.
Warning: By default, the system does not retain the changes permanently. Once you restart a Linux Server, the newly modified state will be lost.
There are two ways to make your adjustments permanent: 1. add the commands to a startup script or 2. edit the distro-specific configuration files.
Manage and Display Network Interfaces
You can get a list of all below-mentioned link command options and more by typing:
ip link help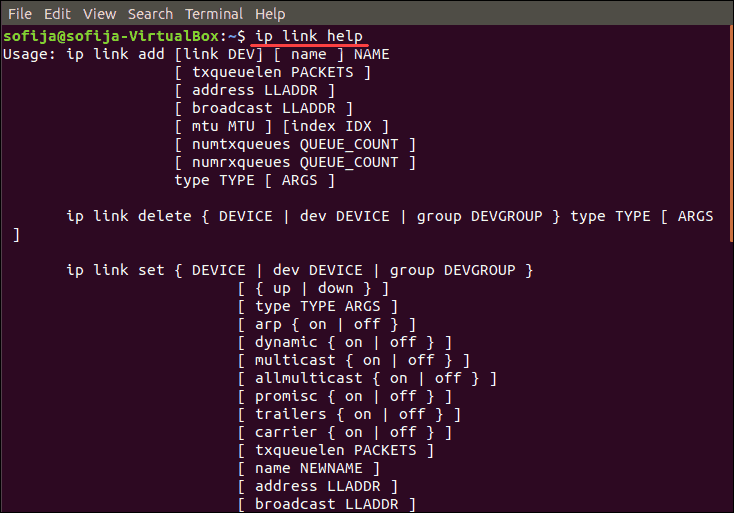
Get Network Interface Information
To see link-layer information of all available devices (which have a driver loaded) use the command:
ip link showIf you want it to display the information for one specific device, type in the following:
ip link show dev [device]To see statistics for all network interfaces (details such as transferred or dropped packets, or even errors) use:
ip -s linkYou can also see similar information for an individual network interface with:
ip -s link ls [interface]In case you need even more details, add another -s to the syntax:
ip -s -s link ls [interface]To see a list of only the running interfaces use:
ip link ls upModify Network Interface Status
If you want to bring a network interface up (online), use the command:
ip link set [interface] upDisable an interface (offline) by entering:
ip link set [interface] downThe ip link command allows you to modify the transmit queue, speeding up or slowing down interfaces to reflect your needs and hardware possibilities.
ip link set txqueuelen [number] dev [interface]You can set the MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) to improve network performance:
ip link set mtu [number] dev [interface]Find all the link command options by typing:
ip link help
Note: Check out our comprehensive Linux network commands list with a downloadable PDF.
Monitor and Manage IP Addresses
Check out all below-mentioned address commands and more by typing the following:
ip addr help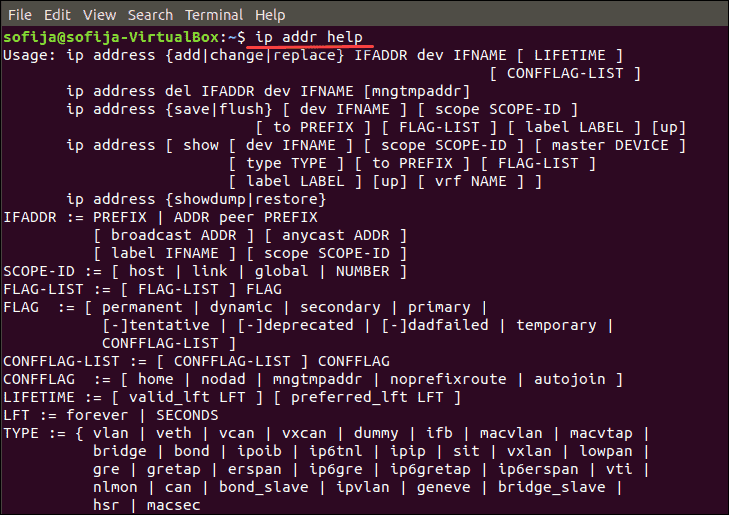
Monitor IP Addresses
Display all devices by using the following command:
ip addrTo list all network interfaces and the associated IP address, use the command:
ip addr showYou can also see information about an individual network:
ip addr show dev [interface]To list the IPv4 addresses, use:
ip -4 addrTo list IPv6 addresses type:
ip -6 addrHow to Add IP Address in Linux
Add an IP address to an interface using the command:
ip addr add [ip_address] dev [interface]Note: If the interface specified does not exist, the output will display the Cannot find device [interface] message.
If you need to add a broadcast address to an interface use the command:
ip addr add brd [ip_address] dev [interface]To remove an IP address from an interface type:
ip addr del [ip_address] dev [interface]Manage and Display IP Routing Table
See a full list of ip route commands with the following command:
ip route help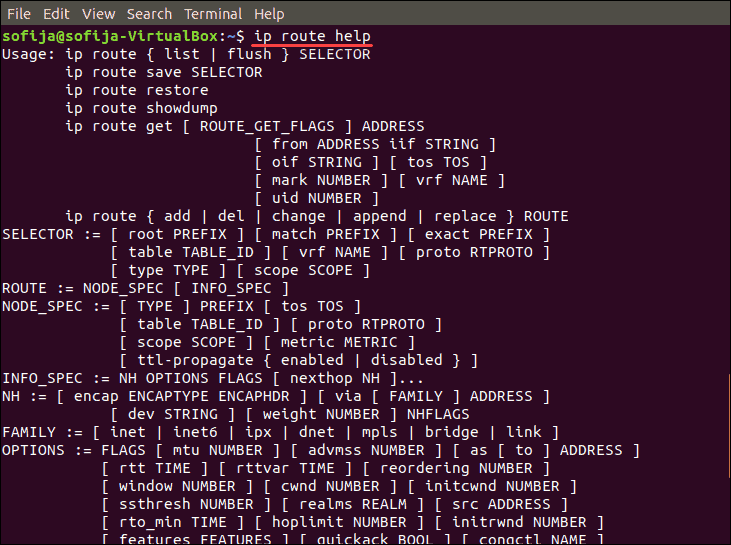
Display IP Routing Table
List all the route entries use either of the following commands:
ip route ip route listWith the commands above, the output displays all of the route entries in the kernel. If you need to narrow down the search, add the SELECTOR object:
ip route list SELECTORNote: SELECTOR := [ root PREFIX ] [ match PREFIX ] [ exact PREFIX ] [ table TABLE_ID ] [ proto RTPROTO ] [ type TYPE ] [ scope SCOPE ]
To view routing for a distinct network, use the following syntax:
ip route list [ip_address]Modify IP Routing Table
To add a new entry in the routing table that can be reached on a specific device, type in the command:
ip route add [ip_address] dev [interface]Or you can add a new route via gateway by typing:
ip route add [ip_address] via [gatewayIP]Also, the command allows you to add a route for all addresses via the local gateway by adding the default option:
ip route add default [ip_address] dev [device]ip route add default [network/mask] via [gatewayIP]To delete an existing entry in the routing table, use the commands:
ip route del [ip_address]ip route del defaultip route del [ip_address] dev [interface]Display and Modify IP Neighbor Entries
Neighbor entries tie the protocol address and the link-layer addresses under the same link. Organized into IPv4 tables, they are also called ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) tables.
For a full list of all neigh command options use:
ip neigh help
Display IP Neighbor Entries
To display neighbor tables, use the following command:
ip neigh showThe output shows the MAC addresses of devices which are part of the system and their state. The state of a device can be:
- REACHABLE – signifies a valid, reachable entry until the timeout expires
- PERMANENT– signifies an everlasting entry that only an administrator can remove
- STALE– signifies a valid, yet unreachable entry; to check its state, the kernel checks it at the first transmission
- DELAY– signifies that the kernel is still waiting for validation from the stale entry
Modify IP Neighbor Entries
Add a new table entry with the command:
ip neigh add [ip_address] dev [interface]Or, remove an existing ARP entry:
ip neigh del [ip_address] dev [interface]Conclusion
You now know what the IP command in Linux is and how to use the command to assist in network/system administration.
Next, discover more Linux Commands in our Cheat Sheet and Tutorial With Examples.